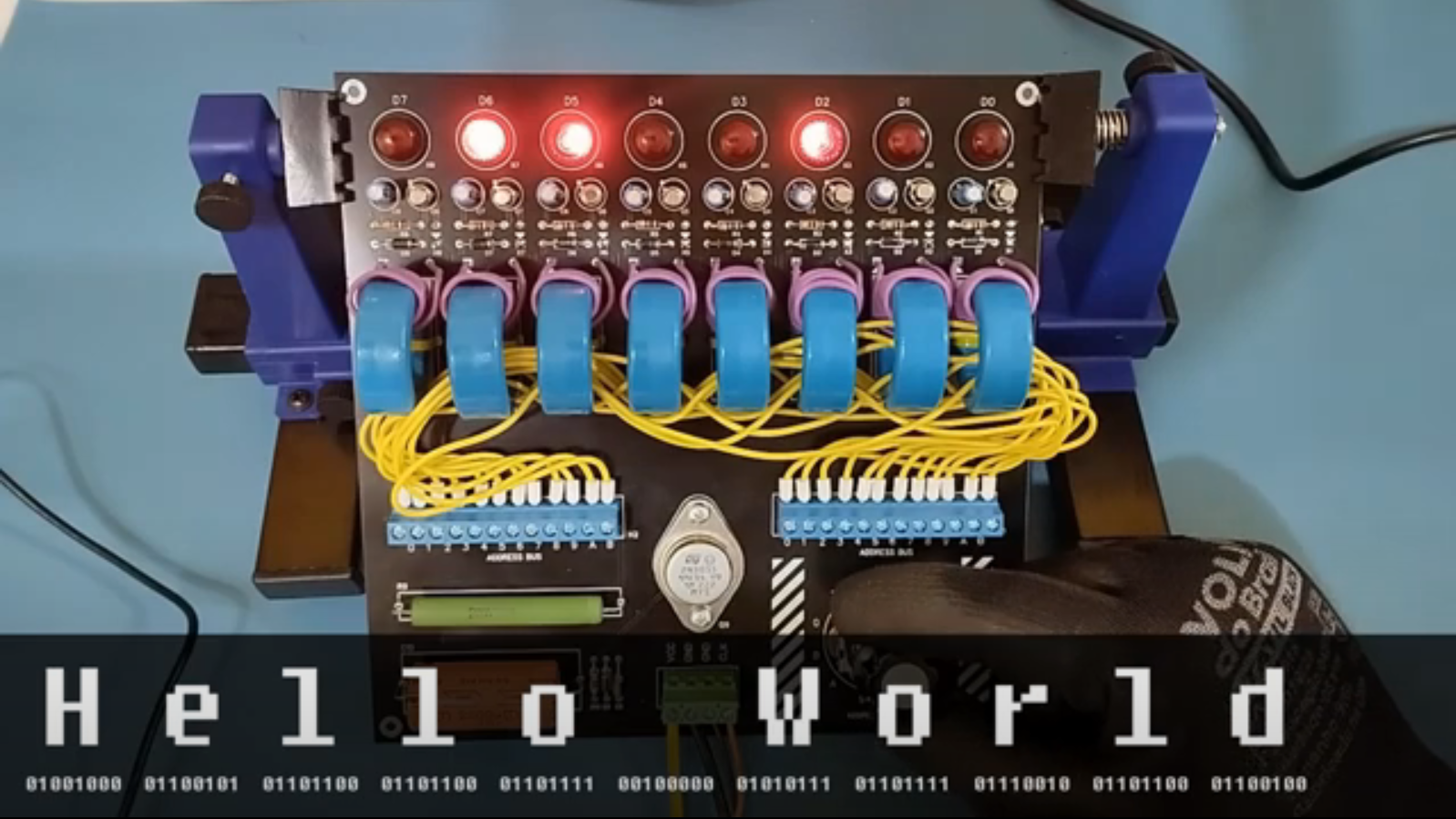
[Luizão] wanted to create some hardware to honour the memory of the technology used to put man on the moon and chose the literal core of the project, that of the hardware used to store the software that provided the guidance. We’re talking about the magnetic core rope memory used in the Colossus and Luminary guidance computers. [Luizão] didn’t go totally all out and make a direct copy but instead produced a scaled-down but supersized demo board with just eight cores, each with twelve addressable lines, producing a memory with 96 bits.
The components chosen are all big honking through-hole parts, reminiscent of those available at the time, nicely laid out in an educational context. You could easily show someone how to re-code the memory with only a screwdriver to hand; no microscope is required for this memory. The board was designed in EasyEDA, and is about as simple as possible. Being an AC system, this operates in a continuous wave fashion rather than a pulsed operation mode, as a practical memory would. A clock input drives a large buffer transistor, which pushes current through one of the address wires via a 12-way rotary switch. The cores then act as transformers. If the address wire passes through the core, the signal is passed to the secondary coil, which feeds a simple rectifying amplifier and lights the corresponding LED. Eight such circuits operate in parallel, one per bit. Extending this would be easy.
Obviously, we’ve covered the Apollo program a fair bit. Here’s a fun tale about recovering the guidance software from the real hardware. Like always, the various space programs create new technologies that we mere mortals get to use, such as an auto-dialling telephone.
(video in Brazilian Portuguese)