Despite being much in the zeitgeist lately, we have to confess to still being a bit foggy about exactly what memristors are. The “mem” part of their name seems to be the important bit, implying a memory function, but the rest of the definition seems somewhat negotiable — enough so that you can make a memristor from a bit of photochromic dye.
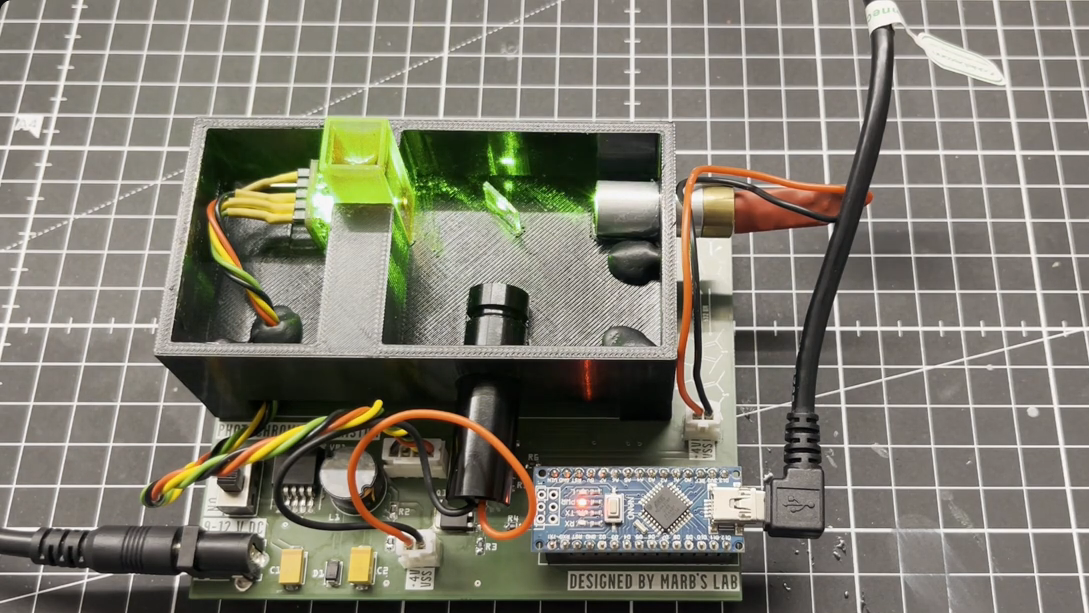
Now, we’ll leave the discussion of whether [Markus Bindhammer]’s rather complex optical memory cell officially counts as a memristor to the comments below, and just go through the technical details here. The heart of this experimental device is a photochromic dye known as cis-1,2-dicyano-1,2-bis(2,4,5-
To accomplish this trick, [Markus] filled a quartz cuvette with a little CMTE-doped epoxy resin. Inside a light-tight enclosure, two lasers — one at 405 nm wavelength, the other at 532 nm — are trained on the cuvette through a dichroic mirror. On the other side of the CMTE resin, he placed a VEML7700 high-accuracy ambient light sensor. An Arduino Nano reads the light sensor and controls the lasers. Writing and erasing are accomplished by turning on the proper laser for a short amount of time; reading the state of the cell involves a carefully timed pulse from the 405 nm laser followed by a 532 nm pulse and watching the output of the sensor.
Is a one-bit memory device that uses a dye that goes for €300 per gram and a pair of laser diodes practical? Of course not, but it’s still pretty cool, and we appreciate all the effort and expense [Markus] went to with this one. Now, if you want some fuel for the “It’s not a memristor” fire, memristors might not even be a thing.