After previously working out a suitable approach to create a period-correct paper tape reader for his tube-based, MC14500B processor-inspired computer, [David Lovett] over at the Usagi Electric farm is back with a video on how he made a working tape reader.

The tape reader’s purpose is to feed data into the tube-based computer, which for this computer system with its lack of storage memory means that the instructions are fed into the system directly, with the tape also providing the clock signal with a constant row of holes in the tape.
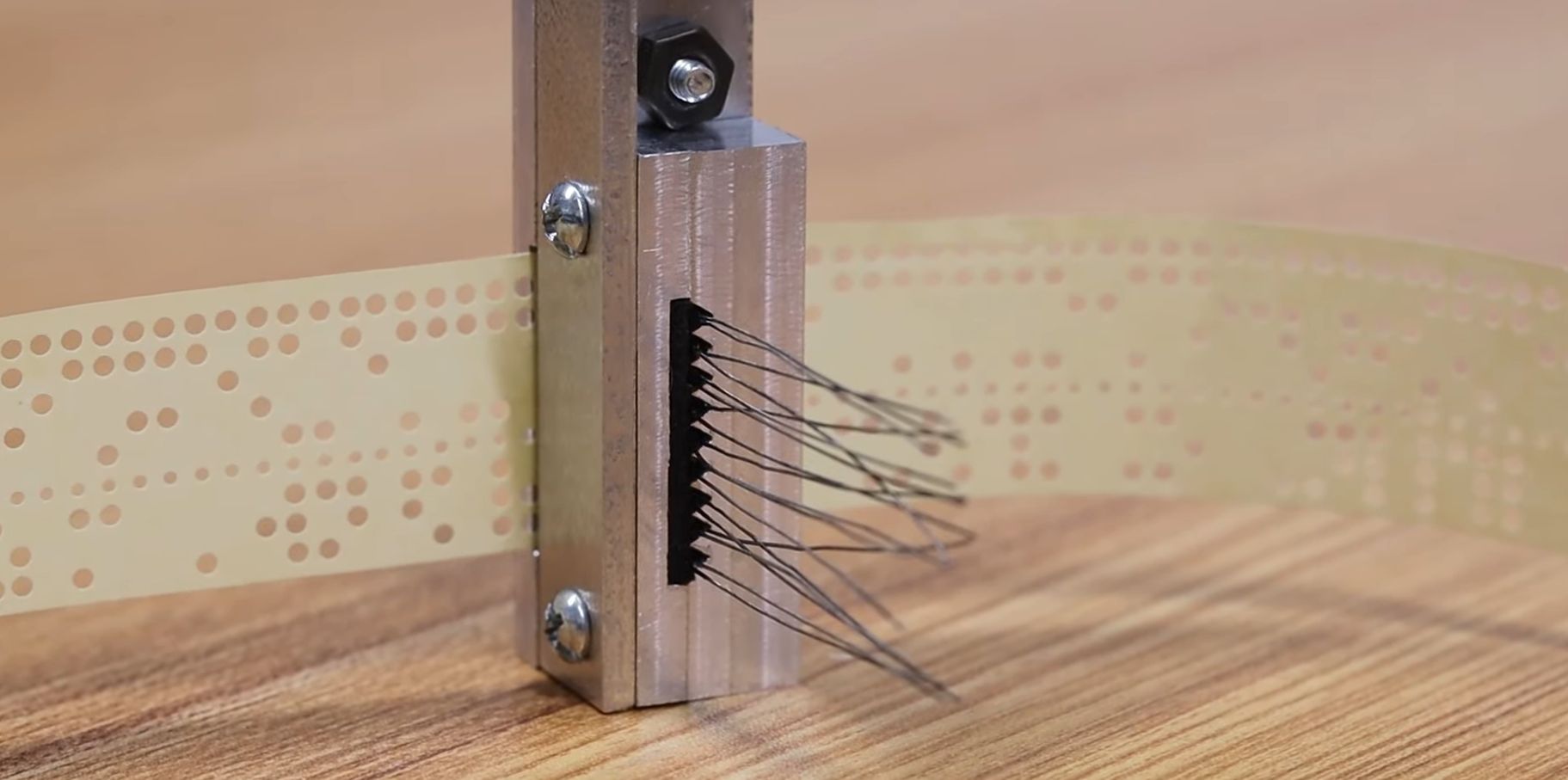
Starting the tape reader build, [David] opted to mill the structural part out of aluminum, which is where a lot of machining relearning takes place. Ultimately he got the parts machined to the paper design specs, with v-grooves for the photodiodes to fit into and a piece to clamp them down. On top of this is placed a part with holes that line up with the photodiodes.
Another alignment piece is added to hold the tape down on the reader while letting light through onto the tape via a slot. After a test assembly [David] was dismayed that due to tolerance issues he cracked two photodiodes within the v-groove clamp, which was a hard lesson with these expensive (and rare) photodiodes.
Although tolerances were somewhat off, [David] is confident that this aluminum machined reader will work once he has it mounted up. Feeding the tape is a problem that is still to be solved. [David] is looking for ideas and suggestions for a good approach within the limitations that he’s working with. At the video’s end, he mentions learning FreeCAD and 3D printing parts in the future. That would probably not be period-correct in this situation, but might be something he could get away with for some applications within the retrocomputing space.
We covered the first video and the thought process behind picking small (1.8 mm diameter) photodiodes as a period-correct tape hole sensor for a 1950s-era computing system, like the 1950s Bendix G-15 that [David] is currently restoring.